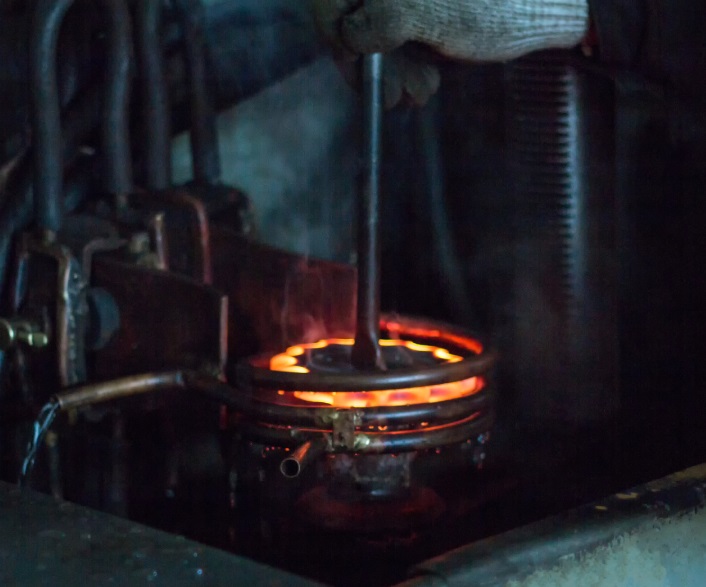

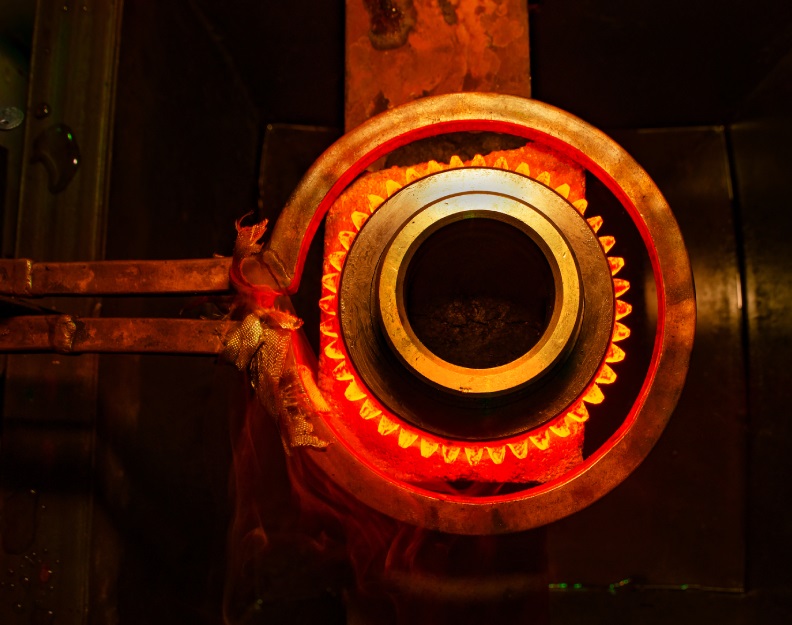

Induction heat treating is a specialized heat treatment process that utilizes electromagnetic induction to heat and transform the properties of metal components.
Unlike conventional heat treatment methods which rely on conduction or convection, induction heating allows for precise and localized heating, resulting in controlled and rapid temperature changes.
This enables targeted treatment of specific areas of a component, ensuring optimal material transformation.
Induction hardening is a widely utilized service in which specific areas of a metal component are selectively heated and rapidly cooled to achieve increased surface hardness. This process improves wear resistance, extends the lifespan of components, and enhances their ability to withstand high-stress environments.
Induction zone annealing involves heating metal components to specific temperatures and then slowly cooling them to relieve internal stresses. This process enhances the material’s ductility, reduces brittleness, and improves its machinability. Induction annealing is commonly used for applications such as automotive parts, springs, and wire products.
Induction heat treating provides precise and controlled heating, allowing for targeted treatment of specific areas. This enables the optimization of material properties, such as hardness and ductility, in critical regions of the component while maintaining desired characteristics in other areas. The ability to selectively heat and cool specific sections ensures consistent and uniform results.
Induction heat treating minimizes distortion and warpage compared to conventional heat treatment methods. Localized heating and rapid cooling reduce thermal gradients and minimize the risk of material deformation. This results in improved dimensional stability, tighter tolerances, and reduced post-treatment machining requirements.
Induction heat treating is commonly used for various steel alloys, including carbon, alloy, and tool steels.
It enhances steel components’ surface hardness, wear resistance, and strength, making them suitable for applications such as gears, shafts, bearings, and cutting tools.